How to Build an Effective and Engaging AI Healthcare Chatbot
For instance, DeepMind Health, a pioneering initiative backed by Google, has introduced Streams, a mobile tool infused with AI capabilities, including chatbots. Streams represents a departure from traditional patient management systems, harnessing advanced machine learning algorithms to enable swift evaluation of patient results. This immediacy empowers healthcare providers to promptly identify patients at elevated risk, facilitating timely interventions that can be pivotal in determining patient outcomes. Initially, chatbots served rudimentary roles, primarily providing informational support and facilitating tasks like appointment scheduling. The validity of the evidence extracted from the included studies was also affected by limitations in the structure of this review. The SF/HIT was used to provide a structured set of whole system implementation outcomes to evaluate the conversational agents [31].
Artificial intelligence is already in our hospitals. 5 questions people want answered – The Conversation
Artificial intelligence is already in our hospitals. 5 questions people want answered.
Posted: Wed, 29 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The integration of Conversational AI in healthcare is not just a trend but a necessity. Its ability to enhance patient engagement, streamline administrative tasks, and improve healthcare access is transforming the industry. As technology evolves, the potential for AI in healthcare is boundless, promising a future of enhanced patient care and operational efficiency.
Navigating the emergence of Generative AI in health care
They have become versatile tools, contributing to various facets of healthcare communication and delivery. Chatbots embedded in healthcare websites and mobile apps offer users real-time access to medical information, assisting in self-diagnosis and health education (5). In technical terms, conversational AI is a type of AI that has been designed to enable consumers to interact with human-like computer applications. Primarily, it has taken the form of advanced-level chatbots to enhance the experience of interacting with traditional voice assistants and virtual agents. Finally, conversational AI enables improved patient engagement by giving them more options to communicate with their healthcare providers, while also helping providers collect feedback from patients about their experience or care plan. This feedback can then be used to both improve patient satisfaction ratings and lead to better overall health outcomes.
To help bring these changes to healthcare, organizations must learn how to use gen-AI platforms, evaluate recommendations, and intervene when the inevitable errors occur. Healthcare organizations may need to provide learning resources and guidelines to upskill employees. And within hospitals and physician group settings—where burnout is already high—leaders should find ways to make gen-AI-powered applications as easy as possible for frontline staff to use, without adding to their workloads or taking time away from patients. Even with all the precautions that applying gen AI to the healthcare industry necessitates, the possibilities are potentially too big for healthcare organizations to sit it out. In this article, we outline the emerging gen-AI use cases for private payers, hospitals, and physician groups. Many healthcare organizations are more likely to start with applying gen AI to administrative and operational use cases, given their relative feasibility and lower risk.
Top 10 Use Cases of Conversational AI in the Healthcare Industry
The agent provides brief interactions to support the person with diabetes in goal setting, action planning and then, following up and asking relevant questions about progress with the self-management of diabetes. Conversational agents, such as ‘Laura’ can have multiple uses in supporting people who are living with chronic conditions. They can even provide emotional and social support, use effective behaviour change techniques to improve current health behaviours, such as physical activity, healthy eating, medication adherence [
49
]. In addition to supporting individuals, conversational agents may also save the healthcare system costs by reducing unnecessary hospital attendance and emergency department visits [
50
].
Quasi-experimental demonstrates the involvement of real-world interventions, instead of artificial laboratory settings. It allows the research to move with higher internal validity than other non-experimental types of research. In addition, quasi-experimental design requires fewer resources and is less expensive compared with RCT.
Revolutionizing Healthcare with Conversational AI: A Comprehensive Guide
The criteria included primary research studies that focused on consumers, caregivers, or healthcare professionals in the prevention, treatment, or rehabilitation of chronic diseases using CAs, and tested the system with human users. Reviews, perspectives, opinion papers, or news articles were excluded based on exclusion criteria. In addition, studies that reported on evaluations based on human users interacting with the entire health system were excluded.
Milne-Ives and colleagues conducted a review on the general effectiveness of AI-empowered conversational agents in healthcare through synthesizing findings from experiments and trials. They found that only three-quarters out of 31 identified studies reported positive or mixed evidence of effectiveness in clinical or behavioural outcomes, and only five studies evaluated the cost-effectiveness of the program. Studies with robust design and comprehensive evaluation are desperately needed to provide evidence before scaling up the innovations into the real-world setting (47). From appointment booking, locating the closest in-network healthcare provider and understanding diagnostic procedures to providing personalized medical information, AI-powered virtual assistants can be immensely valuable for patients and healthcare providers alike.
In the US, about 60% of adults have chronic diseases, causing the annual health care expenditure approximately 86.2% of the $2.6 trillion [20]. In 2018, the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare claims that diabetes is one of Australia’s eight common chronic conditions, contributing to 61% of the disease burden, 37% of hospitalizations, and 87% of deaths [21]. There are about 1.13 billion people who had suffered from hypertension in 2015, and the number is still increasing. All statistics about chronic conditions show how serious they are and their effect on people’s lives [19].
Managing AI Risks in Healthcare; GPT-4’s Clinical Biases; DIY AI Clinic – Medpage Today
Managing AI Risks in Healthcare; GPT-4’s Clinical Biases; DIY AI Clinic.
Posted: Thu, 28 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
One notable algorithm in the field of federated learning is the Hybrid Federated Dual Coordinate Ascent (HyFDCA), proposed in 2022 (14). HyFDCA focuses on solving convex optimization problems within the hybrid federated learning setting. It employs a primal-dual setting, where privacy measures are implemented to ensure the confidentiality of client data. By using HyFDCA, participants conversational ai in healthcare in federated learning settings can collaboratively optimize a common objective function while protecting the privacy and security of their local data. This algorithm introduces privacy steps to guarantee that client data remains private and confidential throughout the federated learning process. With instant, accurate responses and personalized care, patient satisfaction soars.
Of these studies, 45% (14/31) evaluated conversational agents that had some type of audio or speech element. The final 2 comprised a contextual question-answering agent and a voice recognition triage system. Conversational agents have been developed for many different aspects of the health sector to support health care professionals and the general public. Specific uses include screening for health conditions, triage, counseling, at-home health management support, and training for health care professionals [8,13-15].
Further, it is unclear how the performance of NLP-driven chatbots should be assessed. The framework proposed as well as the insights gleaned from the review of commercially available healthbot apps will facilitate a greater understanding of how such apps should be evaluated. As technology continues to power more health care processes, gen AI likely stands at the forefront of this transformation, with the potential for unprecedented advancements in consumer engagement, patient care, and operational efficiencies. Here, it is important to highlight the fact that conversational AI is not just a chatbot, though these terms are often used interchangeably.
Clinical, Legal, and Ethical Aspects of Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Conversational Agents in Health Care
To help train the bot effectively, it is important to collect real user data or as close to how real users would ask in every day virtual assistant queries. These go beyond mere rule-based answers to analyse text and speech, understand intent and context, generate responses and continually learn from queries in order to carry out actual conversations with a user like a human. Almost two-thirds of the studies (19/31) used samples of less than 100 participants or items of analysis (eg, voice clips and clinical scenarios) with a median sample size of 48 across all the studies. Many also did not sufficiently report demographic data or whether their sample was representative of their target population. Although many of these studies were early feasibility and usability trials, this is an important issue to address in future research testing these agents to determine whether an agent will be used and used effectively by its target population. Summary of the studies based on the evaluation outcomes from the synthesis framework for the assessment of health information technology differentiating between positive and mixed outcomes.
Because of this, healthcare leaders should begin thinking about how they can improve their data’s fidelity and accuracy through strategic partnerships—with providers, payers, or technology vendors—and interoperability investments. In conclusion, Conversational AI is an emerging technology that has the potential to transform the healthcare industry. Our discussion has highlighted both the pros and cons of implementing Conversational AI in a healthcare organization and explored its role in improving patient experience, customer service, and engagement. Based on the information given, the AI virtual assistant can advise on seeking immediate medical attention, scheduling appointments, or considering at-home remedies. Additionally, this ensures standardized guidance rooted in established medical protocols, streamlining patient care. The intricacies of billing, insurance claims, and payments can be a source of stress.
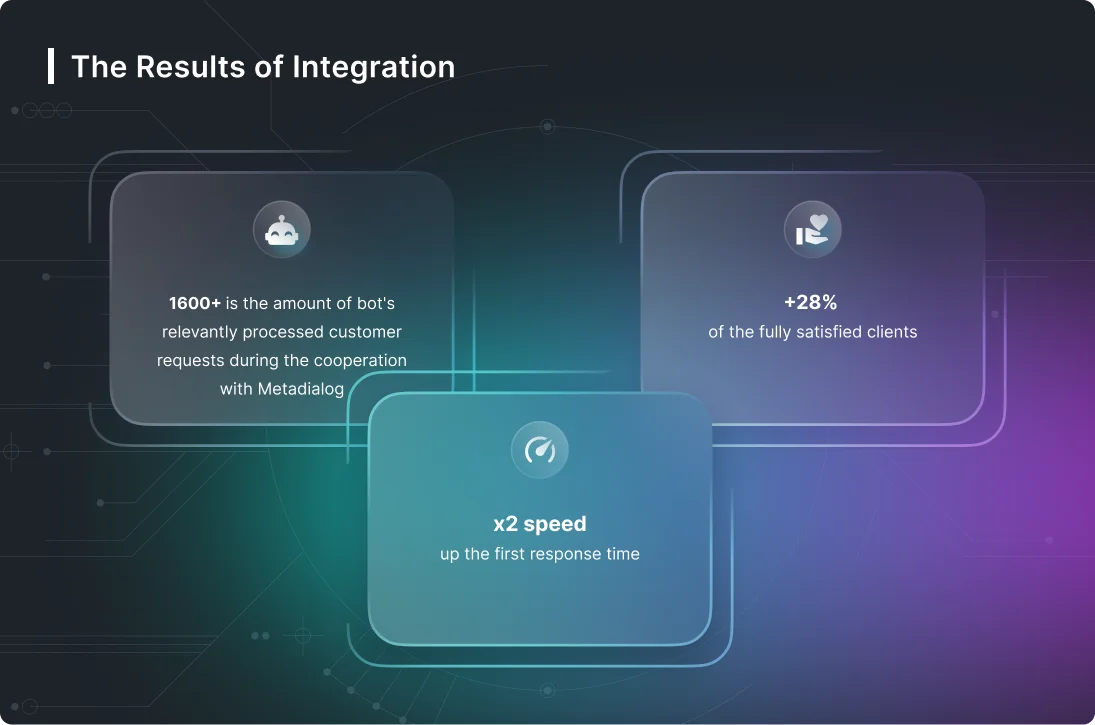
They also have designated compliance personnel who respond promptly and take corrective action to offenses. Despite the challenges that are unique to the industry, healthcare institutions can get all the benefits of a conversational AI solution by approaching it with the right strategy. This involves 3 key phase – Discovery, Implementation and Refinement, and Integration.
- This also ties into the “philosophy of care” practiced in the region and even in the specific hospital.
- Our review reflected this as most of the included studies were published after 2016 (21 papers).
- This step involves mapping out and curating all the possible answers that the bot can return.
- In fact (depending on the industry and specific business of course), we’ve found that on average only about 5% of people actually fill out CSAT surveys.
